My interview on the geopolitical situation 25 years after the fall of the Berlin Wall:
My interview on the geopolitical situation 25 years after the fall of the Berlin Wall:

A comment piece from last week on RT about German politicians wanting to go back to paper-based communications to evade the US spy panopticon:
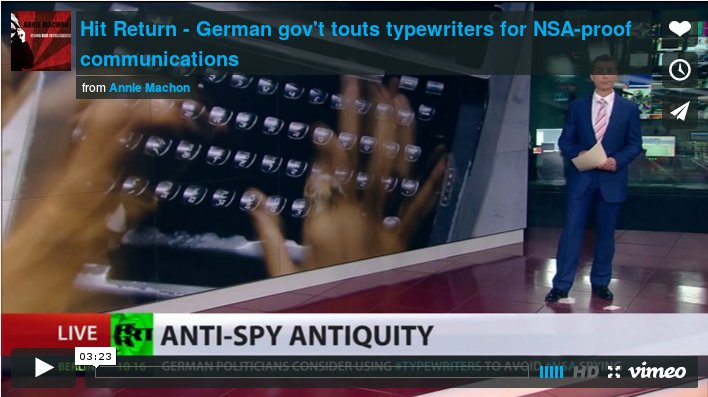
And here is the full text of the interview I gave on RT Op Edge:
Both typewriter and strong encryption is going to slow down communication, but upholding a basic democratic right of privacy seems to be more important, former MI5 agent Annie Machon told RT.
Amid the American-German espionage scandal, German politicians are considering going back to old-fashioned manual typewriters for confidential documents in order to protect national secrets from American NSA surveillance.
RT: Why would Germany think of using typewriters as a security measure?
Annie Machon: What I find interesting is that we have a situation where even our democratically elected representatives have to think deeply and seriously about how to protect the privacy of their communications, particularly when the investigation of the very subject of invasion of the privacy of the citizens, which is what the Bundestag at the moment is doing in Germany, trying to hold hearings to work out what exactly the NSA has been doing, which might be contravening the constitution of Germany. It is very difficult now but it is still possible to protect your electronic communications, but I think this announcement, this sort of statement by the Bundestag representative about going back to typewriters is interesting. It just makes a very strong point that we all need to be aware of the fact that we can be spied on at any time.
RT: Do you think everyone would follow Germany’s example?
AM: I think more and more people are concerned about their privacy because of the Edward Snowden disclosures. He has done the world a huge service with great personal cost, exposing the predations of the US Intelligence agencies and the NSA particularly, as well as a number of European agencies. In the past all countries spied on each other because they wanted to gain advantage over other countries, not necessarily their enemies, just an advantage economically or politically. However, what we are seeing at the moment is the result of what was the perfect storm for the USA in the 1990s, it was a perfect opportunity for them, because at that point the Cold War had ended, they were the sole remaining superpower on the planet, and precisely at that moment we had the evolution of the internet, a huge tech explosion of communications. They saw the opportunity and they went for it. Of course they did because that meant that they could embed whatever they wanted into the infrastructure that the whole world now uses for communication. Of course they were not going to turn this opportunity down, and they haven’t. That is what Edward Snowden disclosed.
So we have the situation now when everything can conceivably be hoovered up by the NSA and its vassal states in Europe, everything can conceivably be stored for ever and be used against citizens in the future if the laws change. And everything can conceivably be known amongst the private deliberations of our parliament’s democratically elected representatives. It’s worse than Orwellian.
It would be naïve to think that the US would not take up this opportunity, but of course they did, and these are the results we are living in. It would be lovely to think that we could go back to the era of having privacy in our lives that our governments would have power to ensure we had it, but in this globalized world it is very difficult to ensure that. One of the things that is little known out of all Snowden’s disclosures is the fact that it is not just what we send over the internet, it is also hardware, the computers, the technology we actually use that can already be compromised by the NSA. This is one of the things that came out just after Christmas last year. So we are living in a very complex world but there are very simple steps we can take, both the governments and the citizens, to protect our democratic and our basic right to privacy.
RT:Wouldn’t using typewriters slow things down in terms of communication? Why not use other, more modern ways of protecting communication?
AM: Either going back to using pen paper or typewriter or using very strong encryption is going to slow down one’s communication, there is no doubt about it. The point is though, what is more important, is it access to the latest celebrity gossip on the internet or is it actually upholding a basic democratic right of privacy. Because if we don’t have privacy, then we lose our freedom to communicate easily and in private, we lose our freedom to ingest information via video, audio or from reading, we cannot plan, we cannot conduct private personal relationships over the internet. So what is the price of a little bit of inconvenience when it comes to protecting our basic rights? I think that however light-heartedly the German politician mentioned using typewriters, when it comes to proper security issues within government, he is probably absolutely right. Last year there was a report as well, saying that some of the Russian security operators were now using typewriters too. We will all have to think about that, and it’s just a jolting wake up call to make us all think about that by stating that the German government is now going back to typewriters for certain things.
RT: What kind of solution do you see? Should people rely on their governments for protection of their privacy?
AM: There is a danger that people and the government will become very paranoid about trying to protect against the predations of the NSA and its vassals in Europe. However, I’m not sure as we as citizens can rely on governments to protect our privacy because all governments would want to know what is going on on the internet for legitimate reasons as well, to try to track down the illegitimate criminals and terrorists. But it can be easy for them to hoover up all the personal information and we, as citizens, need that have that guarantee of privacy. So one of the things we can do as citizens is to take responsibility in our own hands. We can indeed source all technologies, source computers pre-2008 that have not built-in hardware backdoors. We can use decent PGP encryption, we can use Tor to hide what we are looking at in the internet, we can use other encryption methodologies to protect our privacy, and we need to. I think it’s a very interesting crossroads in our history, both as civilizations, as democracy and as individuals, but also how we view the technology, how we use it, how we can better use it to protect our life, so that is going it be an ongoing debate. I’m very pleased to see this in Germany particularly. The politicians seem to be waking up around these issues and wanting debate these issues because the USA has got away with it for long enough across the West.
My recent interview on RT about Ukraine and interventionism, both West and East:

US miscalculated will of Ukrainian people from Annie Machon on Vimeo.
As the news broke that NSA whistleblower, Edward Snowden, had fled Hong Kong for Russia today, I was invited on RT to do an interview. At that point few people had any idea of his plans. However, it appears that the USA had charged Snowden under the Espionage Act 1917 (no surprises) and then asked Hong Kong to arrest and hold him, pending extradition. Equally unsurprisingly, Hong Kong found mistakes in the paperwork and used the opportunity to complain about US spying activity in its territory.
Anyway, this gave Snowden, with apparently the help of the whistleblowing publishing site Wikileaks, the chance to leave the country and fly to Russia, with the reported final destination being Ecuador.
So here’s my initial take on the situation:
Snowden case shows US is bully boy of world — RTTV interview from Annie Machon on Vimeo.
RT TV interview earlier this afternoon on US deployment of Anti-Ballistic Missile Defence systems in Alaska.
And here’s an interview I did yesterday for Russia Today TV about the the spy story:
 According to the Daily Mail this week, Russian security expert, Andrei Soldatov, reckons the UK is wide open to the threat of the Russian mafia. He primarily blames the froideur that has blighted Anglo-Russian relations since the Litvinenko affair. However, he also states that MI5 no longer has a role to play in investigating organised crime, and that has contributed to our vulnerability.
According to the Daily Mail this week, Russian security expert, Andrei Soldatov, reckons the UK is wide open to the threat of the Russian mafia. He primarily blames the froideur that has blighted Anglo-Russian relations since the Litvinenko affair. However, he also states that MI5 no longer has a role to play in investigating organised crime, and that has contributed to our vulnerability.
Naturally resisting the temptation to say that MI5’s involvement would not necessarily have afforded us any meaningful protection, I would say that this is down to a fundamental problem in how we organise our response to threats to the national security of this country.
The security infrastructure in the UK has evolved over the last century into a terribly British muddle. For historic reasons, we have a plethora of intelligence agencies, all competing for funding, power and prestige: MI5, MI6, GCHQ, the Metropolitan Police Special Branch (MPSB), special branches in every other police force, military intelligence, and HM Revenue and Customs et al. Each is supposed to work with the other, but in reality they guard their territory and intelligence jealously. After all, knowledge is power.
MI5 and MPSB have always been the lead intelligence organisations operating within the UK. As such, their covert rivalry has been protracted and bitter, but to the outside world they appeared to rub along while MI5 was primarily focusing on espionage and political subversion and the Met concentrated on the IRA. However, after the end of the Cold War, MI5 had to find new targets or lose staff, status and resources.
 In 1992 the then Home Secretary, Ken Clarke, announced that MI5 was taking over the lead responsibility for investigating IRA activity on the UK mainland — work that had been done by MPSB for over 100 years. Victory was largely credited to clever Whitehall manoeuvering on the part of the head of MI5, Stella Rimington. The Met were furious, and the transfer of records was fractious, to say the least.
In 1992 the then Home Secretary, Ken Clarke, announced that MI5 was taking over the lead responsibility for investigating IRA activity on the UK mainland — work that had been done by MPSB for over 100 years. Victory was largely credited to clever Whitehall manoeuvering on the part of the head of MI5, Stella Rimington. The Met were furious, and the transfer of records was fractious, to say the least.
Also, there was a year’s delay in the handover of responsibility. So MI5 artificially maintained the perceived threat levels posed by political subversion in order to retain its staff until the transition was complete. This meant that there was no real case for the aggressive investigation of subversive groups in the UK – which made all such operations illegal. Staff in this section, including me, vociferously argued against this continued surveillance, rightly stating that such investigations were thereby flagrantly illegal, but the senior management ignored us in the interests of preserving their empires.
However, in the mid-1990s, when peace appeared to be breaking out in Northern Ireland and beyond, MI5 had to scout around for more work to justify its existence. Hence, in 1996, the Home Secretary agreed that they should play a role in tackling organised crime – but only in a supporting role to MPSB. This was never a particularly palatable answer for the spooks, so it is no surprise that they have subsequently dropped this area of work now that the threat from “Al Qaeda” has grown. Terrorism has always been perceived as higher status work. And of course this new threat has led to a slew of increased resources, powers and staff for MI5, not to mention the opening of eight regional headquarters outside London.
But should we really be approaching a subject as serious as the protection of our national security in such a haphazard way, based solely on the fact that we have these agencies in existence, so let’s give them some work?
If we are really faced with such a serious terrorist threat, would it not be smarter for our politicians to ask the basic questions: what is the realistic threat to our national security and the economic wellbeing of the state, and how can we best protect ourselves from these threats? If the most effective answer proves to be a new, dedicated counter-terrorism organisation, so be it. We Brits love a sense of history, but a new broom will often sweep clean.
